Found 19 resources for the concept:
Science aims to build explanations of the natural world. (P3, P6)
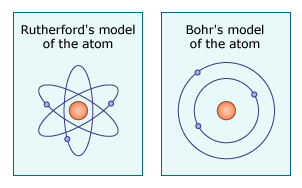
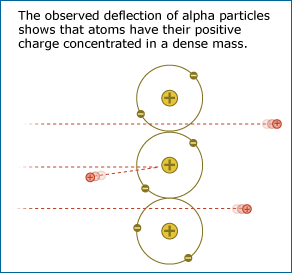
A science prototype: Rutherford and the atom
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
- classroom activity
- Science Story
Discipline:
- Physical Sciences
Time: 30 minutes
Overview
Have your students read the full article on Rutherford's investigations of the atom and compare it to the Science Checklist in order to explore the key traits that make science science. Get more tips on using Science Stories in class.
Age dating star clusters
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
Source:
- Whitfield, Lisé
Resource type:
- lab activity
Discipline:
- Space science
Time: ~ one hour
Overview
Students explore how classification and graphing are used by astronomers to determine the age of star clusters. They will measure the color and brightness of stars, as proxies for temperature and luminosity.
Amazon fly
Grade Level(s):
- 6-8
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
- lab activity
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: 10-15 minutes
Overview
This short activity quickly engages the participants in the process of developing testable hypotheses. Students come up with multiple hypotheses to explain a set of observations and figure out how to test these hypotheses.
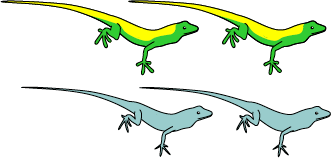
Anolis Lizards
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
Source:
- Collins, Jennifer
Resource type:
- lab activity
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: Two class periods
Overview
Students "travel" to the Greater Antilles to figure out how the Anolis lizards might have evolved there. Students make observations, ask questions, share data, form hypotheses, generate expectations, get more data, interpret them, and test their ideas.
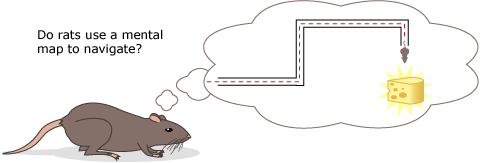
Beyond the prototype: Animal psychology
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
- Science Story
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: 15 minutes
Overview
Have your students read about an investigation of animal navigation and compare it to the Science Checklist in order to explore the key traits that make science science. Get more tips on using Science Stories in class.
Clipbirds
Grade Level(s):
- 6-8
- 9-12
Source:
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
- classroom activity
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: one class period
Overview
In this activity, students simulate bird feeding with "beaks" that differ in size. The proportion of big-, medium-, and small-beaked birds changes in response to available types of food. This is a lesson on evolution, but suggestions on how to incorporate the nature and process of science are included.
Designing your very own science experiment
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
Source:
- Stefanski, Mark
Resource type:
- lab activity
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: 2-4 class periods
Overview
Students design and carry out an experiment using pill bugs (isopods). Other organisms could be used in place of the pill bugs. Students reflect on the process used by charting their pathway on the Science Flowchart.
Endosymbiosis: Cells within cells
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
- Science Story
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: one period
Overview
This Science Story on endosymbiosis explores the career of microbiologist Lynn Margulis and how an unlikely idea overcame strong resistance within the scientific community and finally came to be an accepted part of evolutionary theory. Get tips for using science stories in class.
How science works
Grade Level(s):
- 6-8
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- California Academy of Sciences
Resource type:
- Science Story
- video
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: 10 minutes
Overview
This Science in Action video uses the Understanding Science Flowchart to follow arachnologist Charles Griswold and colleagues as they describe the process involved in an exciting new spider discovery.
Luminous
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- Sam Smartt
Resource type:
- classroom activity
- Science Story
- video
Discipline:
- Space science
Time: 2-8 hours
Overview
The film LUMINOUS (now freely available through many libraries and the Kanopy platform) tells the story of astronomer Larry Molnar as he investigates a distant, double-star system, about which he makes a daring and explosive prediction. Interviews with Dr. Molnar’s diverse set of colleagues, collaborators, and skeptics highlight science as a community and intensely human endeavor, debunking the myth of the lone scientist conducting dispassionate research. The Luminous Science Education Toolkit provides classroom activities to support students' interpretation of the film.
Newton’s 2nd law: Inquiry approach
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
Source:
- Tung, Cecilia
Resource type:
- classroom activity
Discipline:
- Physical Sciences
Time: One to two class periods
Overview
Students act as colleagues of Isaac Newton. Students focus on how to design a procedure to test Newton's hypothesis and then communicate that idea to others. The emphasis is on the process rather than the actual results.
Rutherford’s enlarged: A content embedded NOS activity
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
Source:
- Abd-El-Khalick, Fouad
Resource type:
- lab activity
Discipline:
- Physical Sciences
Time: One class period
Overview
Students reason about a model of Ernst Rutherford's famous experiment supporting the idea of the atomic nucleus. They differentiate between observation and inference and see the role of creativity in the process of science.
The Hobbit: When scientists disagree about the evidence
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- Visionlearning
Resource type:
- classroom activity
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: One class period
Overview
This classroom activity, adapted from an exercise on PBS's NOVA website, provides an excellent example of an active debate within the scientific community regarding a relatively recent human fossil find, Homo floresiensis.
The science checklist applied: CFCs and the destruction of the ozone layer
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
- Science Story
Discipline:
- Earth science
- Physical Sciences
Time: 15 minutes
Overview
Have your students read about the investigation of the hole in the ozone layer and compare it to the Science Checklist in order to explore the key traits that make science science. Get more tips on using Science Stories in class.
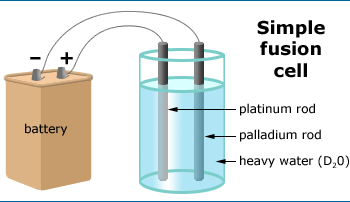
The science checklist applied: Cold fusion
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
- Science Story
Discipline:
- Physical Sciences
Time: 15 minutes
Overview
Have your students read about an investigation of cold fusion and compare it to the Science Checklist in order to explore the key traits that make science science. Get more tips on using Science Stories in class.
The science checklist applied: Solving DNA’s double helix
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
- Science Story
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: 15 minutes
Overview
Have your students read about the investigation of DNA's double helix and compare it to the Science Checklist in order to explore the key traits that make science science. Get more tips on using Science Stories in class.
The science checklist applied: Studying variable stars
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
- Science Story
Discipline:
- Space science
Time: 20 minutes
Overview
Students can use this reading, along with the Science Checklist, to investigate the features that make science science while learning about an early female astronomer. Get tips for using science stories in class.
The story behind the science
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- Iowa State University
Resource type:
- article
Time: Variable
Overview
Thirty stories spanning five disciplines help students explore key science concepts through the eyes of the scientists who were involved, while emphasizing the nature and process of science.
What do you think it means to be human?
Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History
Resource type:
- classroom activity
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: 50 minutes
Overview
This first lesson of the "What does it mean to be human?" sequence sets a scientific frame of mind for students as they begin to explore the question, "What do you think it means to be human?" This lesson sets an important tone by highlighting that other lines of human inquiry outside of science are important for answering this question on a personal level, but the class will focus on a scientific definition of "humanity." Students learn to distinguish questions that could be addressed by the methods of science and those that could not, and they practice applying these criteria.