Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
Source:
- Abd-El-Khalick, Fouad
Resource type:
- lab activity
Discipline:
- Physical Sciences
Time: One class period
Overview
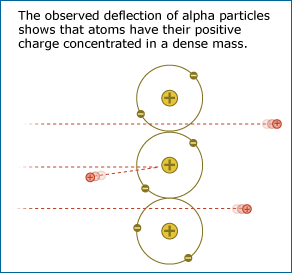
Students reason about a model of Ernst Rutherford's famous experiment supporting the idea of the atomic nucleus. They differentiate between observation and inference and see the role of creativity in the process of science.
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Science is both a body of knowledge and the process for building that knowledge. (NOS5)
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Science aims to build explanations of the natural world. (P3, P6)
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Science focuses on natural phenomena and processes.
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Science works only with testable ideas. (P2, P3, NOS2)
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Scientists strive to test their ideas with evidence from the natural world; a hallmark of science is exposing ideas to testing. (P3, P4, P6, P7, NOS2)
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Scientific knowledge is open to question and revision as new ideas surface and new evidence is discovered. (P4, P6, NOS3)
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Scientific ideas cannot be absolutely proven.
- [How science works: Grades 9-12] The process of science involves observation, exploration, testing, communication, and application.
- [How science works: Grades 9-12] Scientific observations can be made directly with our own senses or may be made indirectly through the use of tools.
- [How science works: Grades 9-12] Scientists test their ideas (hypotheses and theories) by figuring out what expectations are generated by an idea and making observations to find out whether those expectations are borne out. (P4, P6)
- [How science works: Grades 9-12] Scientists can test ideas about events and processes long past, very distant, and not directly observable.
- [How science works: Grades 9-12] Scientists use multiple research methods (experiments, observational research, comparative research, and modeling) to collect data. (P2, P3, P4, NOS1)
- [How science works: Grades 9-12] Raw data must be analyzed and interpreted before we can tell whether a scientific idea is likely to be accurate or inaccurate. (P4, P5)
- [How science works: Grades 9-12] Analysis of data usually involves putting data into a more easily accessible format (visualization, tabulation, or quantification of qualitative data). (P4, P5)
- [The social side of science: Grades 9-12] Scientists are creative. (NOS7)
- NOS Matrix understanding category 1. Scientific investigations use a variety of methods.
- NOS Matrix understanding category 2. Scientific knowledge is based on empirical evidence.
- NOS Matrix understanding category 3. Scientific knowledge is open to revision in light of new evidence.
- NOS Matrix understanding category 5. Science is a way of knowing.
- NOS Matrix understanding category 7. Science is a human endeavor.
- Science and Engineering Practice 2. Developing and using models
- Science and Engineering Practice 4. Analyzing and interpreting data
- Science and Engineering Practice 5. Using mathematics and computational thinking
- Science and Engineering Practice 6. Constructing explanations and designing solutions
- Science and Engineering Practice 7. Engaging in argument from evidence
Intertwining nature of science and content instruction might make learning about the nature and process of science more meaningful for students and might help teachers overcome time constraints.