Grade Level(s):
- 9-12
- College
Source:
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
- Science Story
Discipline:
- Life Science
Time: 15 minutes
Overview
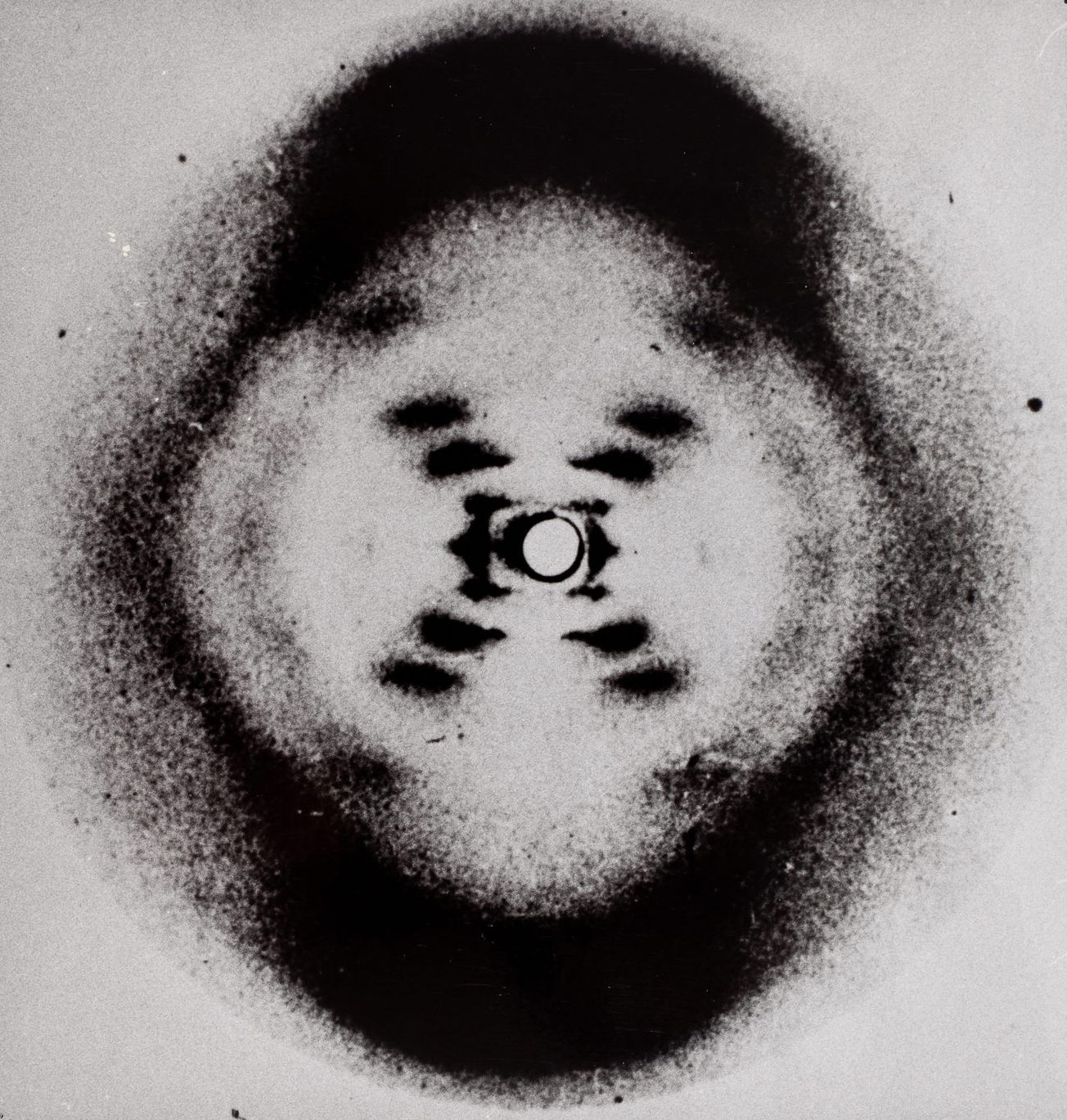
Have your students read about the investigation of DNA's double helix and compare it to the Science Checklist in order to explore the key traits that make science science. Get more tips on using Science Stories in class.
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Science aims to build explanations of the natural world. (P3, P6)
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Science focuses on natural phenomena and processes.
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Science works only with testable ideas. (P2, P3, NOS2)
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Scientists strive to test their ideas with evidence from the natural world; a hallmark of science is exposing ideas to testing. (P3, P4, P6, P7, NOS2)
- [What is science?: Grades 9-12] Science is ongoing; answering one scientific question frequently leads to additional questions to be investigated. (P1)
- [What is science?: Grades 13-16] Science aims to build increasingly broad and coherent explanations of the natural world.
- [What is science?: Grades 13-16] Science focuses on natural phenomena and processes.
- [What is science?: Grades 13-16] Science works only with testable ideas.
- [What is science?: Grades 13-16] Scientists strive to test their ideas with evidence from the natural world; a hallmark of science is exposing ideas to testing.
- [What is science?: Grades 13-16] Scientific knowledge is open to question and revision as new ideas surface and new evidence is discovered.
- [What is science?: Grades 13-16] Science is ongoing; answering one scientific question frequently leads to additional questions to be investigated.
- [The social side of science: Grades 9-12] Science depends on communication within the scientific community. (P7, P8)
- [The social side of science: Grades 13-16] Science depends on communication within the scientific community.
- NOS Matrix understanding category 2. Scientific knowledge is based on empirical evidence.
- Science and Engineering Practice 1. Asking questions and defining problems
- Science and Engineering Practice 2. Developing and using models
- Science and Engineering Practice 4. Analyzing and interpreting data
- Science and Engineering Practice 6. Constructing explanations and designing solutions
- Science and Engineering Practice 7. Engaging in argument from evidence
- Science and Engineering Practice 8. Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information
There are currently no teaching tips for this resource.